Application of GIS, Remote Sensing, IoT, and AI in Natural Resource Management
30-06-2025 09:54
In the context of accelerating climate change and forest degradation, the application of digital technologies in forest resource management has become both an inevitable trend and an urgent necessity. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the integration of advanced technologies—namely Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Remote Sensing (RS), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Artificial Intelligence (AI)—in forestry management, with a particular focus on practical applications in Vietnam and comparisons with global trends.
 Model for applied AI, IOT, GIS, RS
Model for applied AI, IOT, GIS, RS
By synthesising theoretical frameworks and analysing real-world case studies, the article highlights the distinct roles each technology plays within the monitoring–forecasting–response–decision-making cycle. Specifically, GIS offers a spatial data infrastructure that supports multi-layered mapping and precise identification of hotspots, aiding in strategic planning and resource governance. Remote Sensing provides temporally continuous satellite imagery, enabling the detection of forest loss, vegetation health assessment, and ecosystem change monitoring. IoT facilitates real-time data collection from the field through wireless sensor networks, capturing information on microclimatic conditions such as humidity, temperature, and smoke—thus supporting early fire warnings and anomaly detection. AI functions as an intelligent engine for processing big data, capable of classifying satellite imagery, recognising patterns in visuals and audio, and modelling forest change scenarios based on socio-environmental factors.
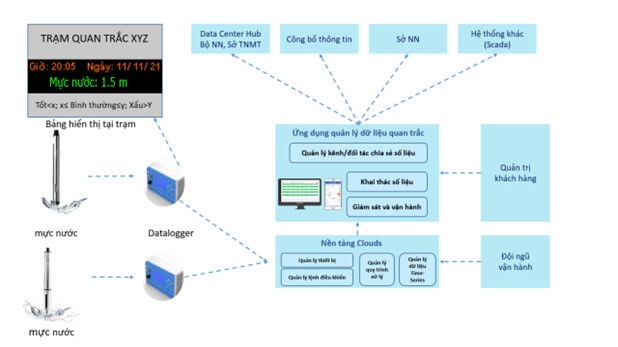
Realtime model for temperature and water level
Alongside these promising applications, the article also addresses key implementation challenges in Vietnam. These include limitations in technological infrastructure and network connectivity in remote forest areas, a shortage of tech-savvy forestry professionals, difficulties in data standardisation and sharing, legal ambiguities surrounding digital evidence and privacy, and concerns over the long-term sustainability of smart systems due to high operational costs. In response, the study proposes a roadmap towards a fully digitised forestry sector—“Forestry 4.0”—that consolidates multi-technology platforms within a unified data ecosystem, calling for policy reform, capacity building, and enhanced international cooperation.
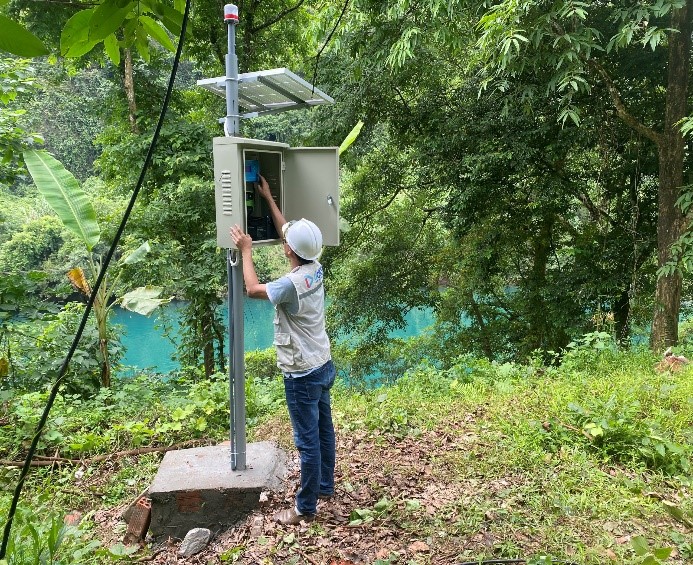 Setup the temperature and water level system
Setup the temperature and water level system
In conclusion, the article affirms that the synergistic integration of GIS, Remote Sensing, IoT, and AI not only enhances the efficiency of forest resource management, but also plays a pivotal role in fostering transparency, institutional innovation, and the sustainable development of Vietnam’s forestry sector in the digital age.
Download the paper of Application of GIS, Remote Sensing, IoT, and AI in Natural Resource Management
Author: Võ Văn Trí
Email: pnkb.vovantri@gmail.com
Thế giới động vật hang động Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng
Khám phá thế giới động vật hang động Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng: cá mù Hang Va, tôm càng Phong Nha, bọ cạp Thiên Đường, ốc nón Sơn Đoòng và các loài mới cho khoa học trong karst.
Đặc điểm và giá trị toàn cầu của hệ thống hang động karst Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng
Phong Nha - Kẻ Bàng có tuổi karst cổ, cấu trúc nhiều hệ thống hang lớn, phân tầng và hình thái đa dạng của Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng, đối chiếu với các di sản hang động tiêu biểu thế giới.
Karst Cave Formation: The Case of the Phong Nha–Ke Bang Limestone Massif
This article explores the karst cave formation process in the Phong Nha – Ke Bang limestone massif, highlighting geological stages shaped by water, tectonics, and tropical climate over millions of years.
Hệ Thống Cảnh Báo Sớm: Lá Chắn Mềm Trước Thiên Tai
Trong bối cảnh khí hậu toàn cầu ngày càng nóng lên và các hiện tượng thời tiết cực đoan gia tăng, thiên tai ở Việt Nam đang gây thiệt hại nặng nề về người và tài sản. Bài viết phân tích vai trò của hệ thống cảnh báo sớm thiên tai như một “lá chắn mềm” giúp giảm nhẹ rủi ro






