Disaster Monitoring System applied for Phong Nha - Ke Bang
28-06-2025 10:45
Võ Văn Trí1, Trần Xuân Mùi 1 Cao Thị Thanh Thủy 2,
1 Phong Nha Ke Bang National Park; 2Quang Binh University
Email: pnkb.vovantri@gmail.com
The disaster monitoring model for Phong Nha – Ke Bang National Park is developed based on Geographic Information System (GIS) technology, utilizing remote sensing data and Digital Elevation Models (DEM) as primary input sources. These datasets are processed and analyzed within the ArcGIS Desktop environment to simulate and forecast disaster scenarios such as flooding, forest fires, and landslides. The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) method is employed to assign weights to various contributing factors for landslide susceptibility, including topography, slope gradient, river density, and vegetation cover. Similarly, fire risk is assessed using the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), land surface temperature, and vegetation density, while flood risk is analyzed through terrain depressions and historical hydrological data.
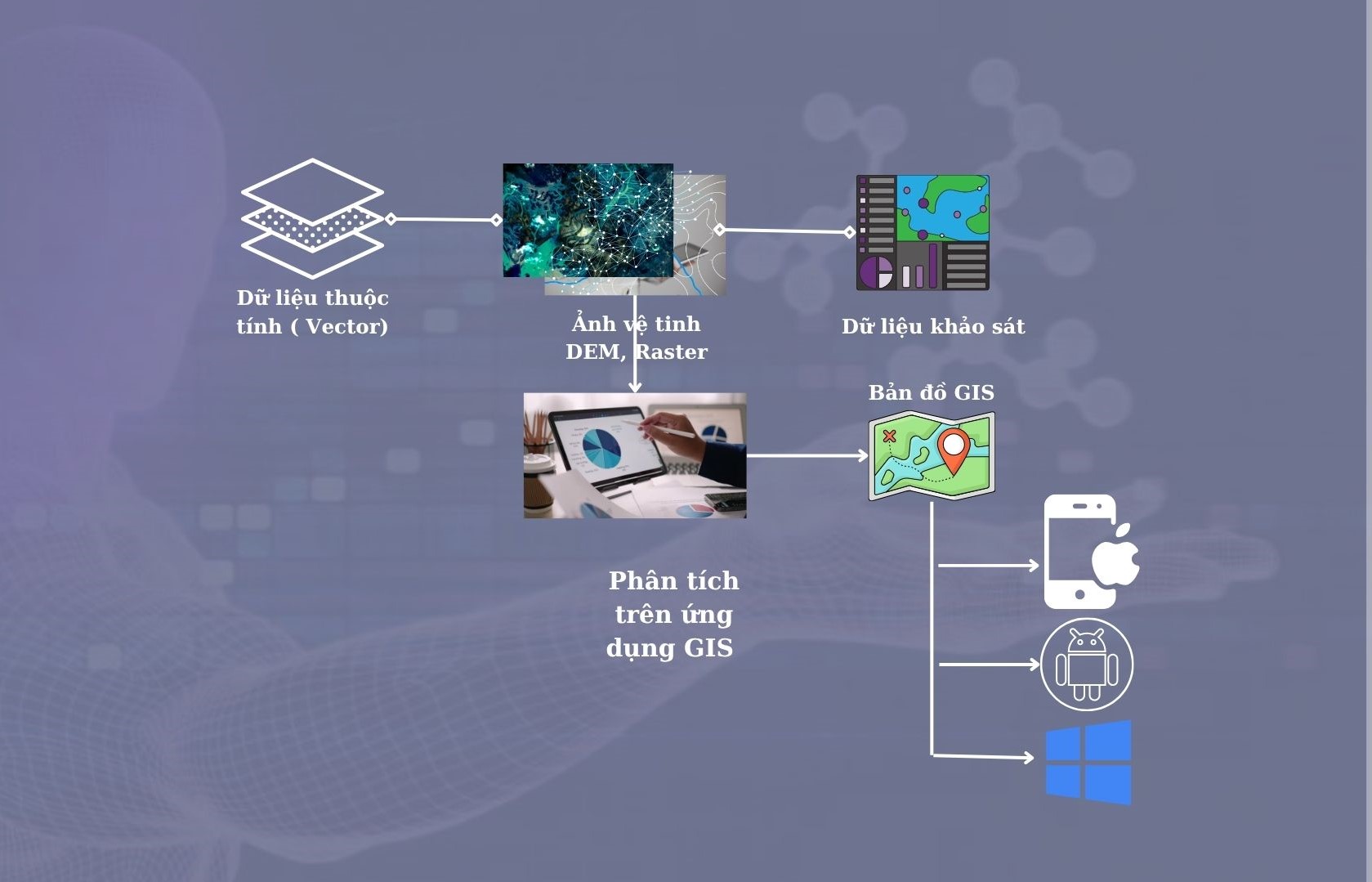 Workflow for Constructing a GIS-Based Natural Disaster Surveillance System
Workflow for Constructing a GIS-Based Natural Disaster Surveillance System
The study successfully generates multi-hazard risk zoning maps. Specifically, the landslide susceptibility map is categorized into five risk levels, with very high-risk zones concentrated along steep mountain slopes near the Ho Chi Minh Road and Route 20 Quyet Thang. The fire risk map identifies highly vulnerable areas in ecological restoration subzones and the eastern periphery of the park, where vegetation cover is sparse and tourism activities are concentrated. The flood risk map indicates that high-risk zones are primarily located in low-lying areas, including Phong Nha township and Sinh Ton Valley.
The GIS- and remote sensing-based disaster monitoring model developed for Phong Nha – Ke Bang National Park holds both scientific and practical significance. Scientifically, it advances integrated methodologies for spatial data analysis, remote sensing applications, and decision-support systems in early warning of natural hazards. The application of the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) enhances the model's accuracy and reproducibility by quantitatively assessing the influence of geo-ecological factors on hazard risks. Practically, the model empowers park management authorities with a proactive tool for disaster preparedness and mitigation, thereby reducing losses to human life and forest resources. Additionally, it lays a foundation for real-time risk management that is transparent, participatory, and shareable across stakeholders, supporting conservation planning and sustainable tourism development. The model is scalable and transferable to other ecologically sensitive areas, contributing to national strategies for climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction.
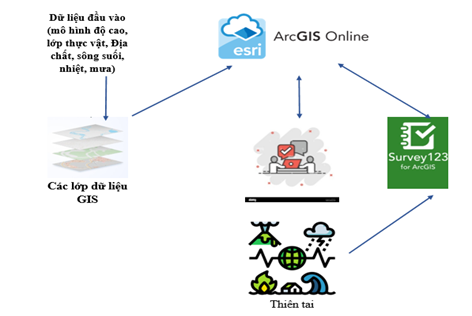
Workflow for Disaster Monitoring System
Link of the paper download here
Author contact by email: pnkb.vovantri@gmail.com
Thế giới động vật hang động Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng
Khám phá thế giới động vật hang động Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng: cá mù Hang Va, tôm càng Phong Nha, bọ cạp Thiên Đường, ốc nón Sơn Đoòng và các loài mới cho khoa học trong karst.
Đặc điểm và giá trị toàn cầu của hệ thống hang động karst Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng
Phong Nha - Kẻ Bàng có tuổi karst cổ, cấu trúc nhiều hệ thống hang lớn, phân tầng và hình thái đa dạng của Phong Nha – Kẻ Bàng, đối chiếu với các di sản hang động tiêu biểu thế giới.
Karst Cave Formation: The Case of the Phong Nha–Ke Bang Limestone Massif
This article explores the karst cave formation process in the Phong Nha – Ke Bang limestone massif, highlighting geological stages shaped by water, tectonics, and tropical climate over millions of years.
Hệ Thống Cảnh Báo Sớm: Lá Chắn Mềm Trước Thiên Tai
Trong bối cảnh khí hậu toàn cầu ngày càng nóng lên và các hiện tượng thời tiết cực đoan gia tăng, thiên tai ở Việt Nam đang gây thiệt hại nặng nề về người và tài sản. Bài viết phân tích vai trò của hệ thống cảnh báo sớm thiên tai như một “lá chắn mềm” giúp giảm nhẹ rủi ro






